Essential Examples of Bill of Lading

Understanding the Evolution and significance of Bills of Lading
The bill of lading has advanced much beyond its humble beginnings as a simple receipt. After decades of global trade, it is now vital to international shipping. It is one of the most important documents in the field. Its origins and functioning explain why it is vital for global trade today.
Early Origins and Mediterranean Trade
The history of the bill of lading begins in the bustling Mediterranean ports of the 11th century. Merchants relied more on ships to deliver goods. So, they needed accurate shipping records. The first bills of lading were receipts. They documented the moment ship owners took possession of specific cargo. By the 13th century, these "Bills of Lading" were like modern package tracking slips. They proved that carriers had received specific goods for transport.
Transition from receipt to contract.
As 16th-century maritime trade grew, so did shipping's challenges. Bills of lading became more complex to address this. This paperwork included details on the cargo's condition, ID markers, and delivery destinations. A 1544 record from Cadiz, Spain, described the receipt of 112 bags of allam. It included the condition and delivery location on the River Thames. This detail protects shippers and carriers if they lose or damage cargo. During this time, someone coined the term "clean bill of lading." It meant that we received items in acceptable shape.
Legal Foundations in the 19th Century
The legal recognition of bills of lading made significant progress in the 1800s. In 1810, the Massachusetts Supreme Court ruled that carriers must honour their bills. This decision enhanced the bill of lading. It is now a binding contract for cargo ownership and transport terms. There were still concerns about carrier liability when products were not loaded. But, the document's legal significance was now well established. Key instances, such as Lickbarrow v. Mason, confirmed the bill is a title document. It implies that one can transfer ownership of goods by transferring the bill.
The Modern Bill of Lading
Today, bills of lading still serve their vital purposes. They have adapted to the demands of modern trade. They continue to serve as receipts, transportation contracts, and title documents. Modern versions also ease trade financing, organise shipments, and speed up customs clearance. Their position has grown due to technology that boosts efficiency and prevents fraud.
Breaking Down Essential Bill of Lading Types

Choosing the appropriate bill of lading is critical to a successful shipping operation. Each type has a distinct purpose. They meet different transport needs. Let us look at the primary types and their roles.
Straight bill of lading.
A straight bill of lading is non-negotiable and addresses a certain recipient. This type works best for cases where trusted parties pay for products or ship between each other. Amazon may use straight bills of lading to transfer products between its warehouses. Yet, banks do not accept this document as collateral. They cannot transfer it.
Negotiable bill of lading (Order Bill of Lading)
A negotiable bill of lading transfers ownership of commodities while in transit. This flexibility is vital in international trade. There, cargo may change hands several times. For example, many customers may buy grain cargo from Canada to Japan en route. Banks often use negotiable bills as loan collateral. They are essential for trade financing.
Clean Bill of Lading
A clean bill of lading certifies that the carrier has delivered undamaged goods. The sender received them in good condition. This designation, whether negotiable or not, assures buyers and banks. It means the shipment met quality standards at the time of loading. Clean bills are often required for transactions involving letters of credit.
Claused bill of lading.
If a shipment has visible damage, the provider gives a claused bill of lading. For example, if furniture arrives damaged or with missing parts, the carrier will note it on the bill. This document protects all parties. It defines issues and allocates responsibilities.
Through the bill of lading.
A through bill of lading is for shipments needing many transport methods. A TV from a Korean maker may travel by truck to a port, by ship across the ocean, and by train to its final destination. A single bill of lading for the entire route simplifies tracking and management.
Legal Issues and Landmark Cases
The legal ramifications of bills of lading apply to every shipment and transaction. As legally enforceable contracts, they impose significant repercussions on shippers, carriers, and consignees. Understanding their legal structure is critical to settling conflicts and preserving interests.
Navigating Legal Requirements and Critical Cases
Historical Cases That Shape Modern Use
Two significant instances shaped the legal status of bills of lading. The 18th-century case Lickbarrow v. Mason established them as records of title. They allowed the transfer of ownership even while goods were in transit. Building on this precedent, the 19th-century decision Newson v. Thornton defined bills of lading as proof of shipping contracts. They establish responsibilities for shippers and carriers.
Variations in legal interpretations.
Different nations interpret bills of lading in various ways. This complicates international trade. For example, the treatment of "clean" and "claused" bills differs by jurisdiction. Even minor wording changes might have a major impact on liability for cargo damage or loss. It's critical for compliance and risk management to know these details and keep up with the laws.
Practical Legal Strategies
To avoid risks and stay compliant, firms must record shipment details. This includes exact product descriptions.
Select the appropriate type of bill of lading for each transaction.
Work with legal experts in international trade. Develop relevant clauses and meet jurisdiction-specific regulations.
The digital transformation of bills of lading.
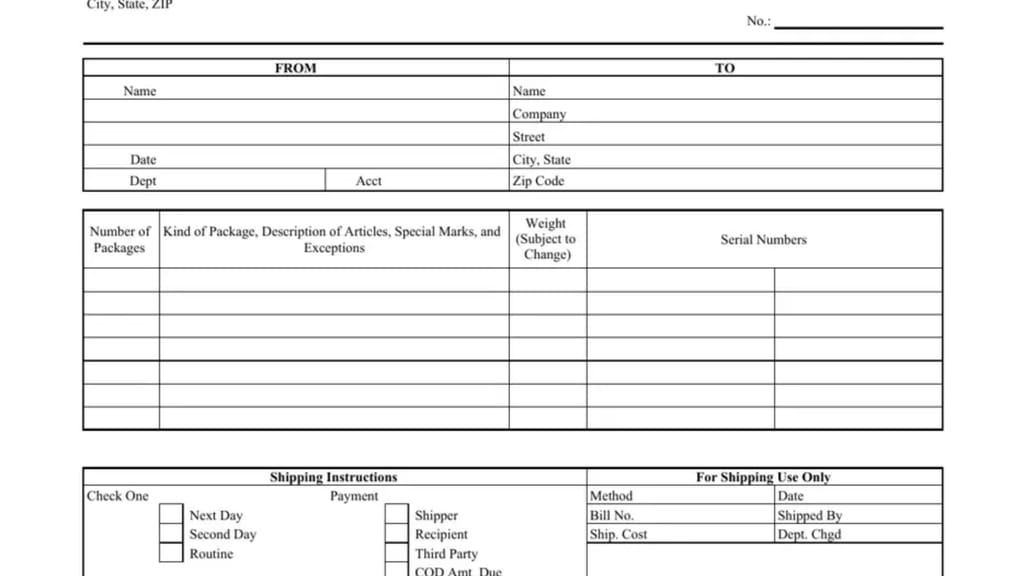
The shift from paper to digital bills of lading (eBLs) is transforming shipping. These electronic documents have got many benefits. They process faster, are less prone to fraud, and are more accessible.
Benefits of Electronic Bills of Lading:
Electronic bills of lading remove delays from handling physical documents. They allow for immediate transfers between parties. They also improve security by using monitoring and access controls. They help avoid forgeries and loss. These characteristics are especially useful for complex international shipments with various stakeholders.
The Role of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology provides an extra degree of security to computerized bills of lading. Blockchain ensures authenticity and fights fraud. It stores each transaction in a tamper-proof, distributed ledger. This technology also improves operations such as customs clearance by automating verification stages.
Adoption Challenges.
Despite their advantages, electronic bills of lading encounter adoption barriers. Legal recognition differs by jurisdiction. So, enterprises must invest in infrastructure and training. The International Chamber of Commerce is trying to set global eBL standards. This will lead to greater acceptance.
Best practices for managing bills of lading.
You must manage bills of lading well for smooth shipping operations. Best practices can boost a business's accuracy, efficiency, and compliance.
Streamlining Documentation
Standardising bill of lading templates promotes consistency and minimises errors. Pre-filling common details, like shipper and consignee info, saves time and boosts accuracy. Integrating bill-of-lading systems with inventory and accounting software boosts efficiency. It does this by automating data flow.

Ensuring accurate descriptions.
Detailed and precise cargo descriptions are essential for avoiding customs delays and conflicts. For example, "20 Dell Latitude 5520 laptops, Serial #XYZ123-XYZ143" is better than "electronics." It avoids confusion.
Supporting Trade Finance
Negotiable bills of lading provide significant advantages for commercial financing. They let banks use them as collateral. This gives sellers quick cash and protects buyers. Keeping proper records of all relevant documents, like invoices and certificates, helps. It aids in this process.
Leveraging Technology
DigiParser and similar tools make it easier to create and maintain e-bills of lading. These technologies automate data extraction and integration. They reduce human work, improve accuracy, and boost communication with other systems.
Conclusion
The bill of lading, with its rich history, is vital to international trade. Its roles have evolved over time. In classic paper form or as an e-document, it is vital for a smooth flow of products across borders. Businesses can optimise their shipping and beat the competition in global trade. They must understand its forms, rules, and best practices.
Transform Your Document Processing
Start automating your document workflows with DigiParser's AI-powered solution.